What are External Integrations?
External Integrations extend ProcessMaker Platform's functionality outside of the BPMN 2.0 specification. An External Integration functions similarly to a Process model element that can be placed and configured in a process model. For example, if your Process model uses the GitHub External Integration, Requests for that Process can read and write data to its configured GitHub repository.
ProcessMaker can integrate with a library of applications and services, including the following:
BambooHR
DocuSign
GitHub
Gmail
Microsoft Excel
Slack
Following Administrative settings must be performed prior to using an External Integration in a process.
From Admin Settings, add the driver for one of the third-party applications and services listed above.
Configure that driver to authenticate with the external integration.
For more information see, Admin Settings for External Integrations.
Add an External Integration to the Process Model
Permissions
Your user account or group membership must have the following permissions to configure a connector unless your user account has the Make this user a Super Admin setting selected:
Processes: Edit Processes
Processes: View Processes
See the Process permissions or ask your Administrator for assistance.
Add an External Integration from one of the following locations in Process Modeler:
Object Panel: Located to the left of the Process Modeler canvas, the Object Panel contains various process model objects.
Object Bar: Located at the bottom of the Process Modeler canvas, the Object Bar contains pinned Process model objects for quick access.
Follow these steps to add an External Integration from the Object panel to the Process model:
Ensure that the Object panel is visible. If not, click the Add icon
 from the Object bar at the bottom.
from the Object bar at the bottom.Click one of the External Integration objects from one of the following sections:
Pinned Objects: The External Integration object appears in the Pinned Objects section when it is pinned.
Object Category: The External Integration object appears in the Object Category section when it is not pinned.
BambooHR

DocuSign

GitHub

Gmail

Microsoft Excel

Slack

Click the location in the Process model to place this external integration. Follow these guidelines when placing this external integration:
Optionally place this external integration between two existing Process model objects already connected with a Sequence Flow element. See Place an object between two connected objects.
If a Pool element is in your Process model, the external integration cannot be placed outside of the Pool element.
Follow these steps to add an External Integration from the Objects bar to the Process model:
Ensure that the object is pinned to the Object bar. If not, pin it.
In the Object bar at the bottom center, click the object's icon. This object's icon displays adjacent to the mouse icon to indicate this external integration may be placed into the Process model.
Click the location in the Process model to place this object. Follow these guidelines when placing this external integration:
Optionally place this external integration between two existing Process model objects already connected with a Sequence Flow element. See Place an Object Between Two Process Model Objects Already Connected with a Sequence Flow Element.
If a Pool element is in your Process model, the external integration cannot be placed outside of the Pool element.
Add boundary events
- Boundary Timer Event element
- Boundary Error Event element
- Boundary Signal Event element
- Boundary Conditional Event element
- Boundary Message Event element
Settings
The connector has the following panels that contain settings:
Properties panel
Loop Activity panel
Query panel
Response Mapping panel
Error Handling panel
Documentation panel
Advanced panel
Configuration Panel Settings
Edit the External Integration Name
An External Integration name is a human-readable reference for a Process model control. Process Modeler automatically assigns the name of a Process model connector with its type. However, a connector's name can be changed.
Follow these steps to edit the name of an External Integration:
Select the External Integration from the Process model in which to edit its name.
Ensure that the Configuration panel displays. If not, show it. Panels to configure this element display.
Expand the Properties panel if it is not presently expanded. The Name setting displays.
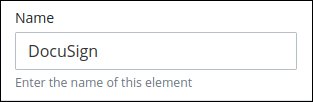
In the Name setting, edit the selected External Integration's name and then press Enter.
Loop Activity Panel Settings
Specify Characteristics to Perform Multiple Instances of the External Integration
Use the Loop Activity panel settings to specify how to perform multiple instances of this External Integration. The following loop modes are available for this External Integration:
No Loop Mode: Select the No Loop Mode option to perform this element's External Integration only once.
Loop: Select the Loop option to sequentially repeat this element's External Integration multiple times until an exit condition is
True. This is useful when a External Integration should be performed multiple times with the same set of data, such as, processing a credit card payment. This loop mode has the following characteristics:The External Integration is repeated until the exit condition is
Trueor the maximum iterations limit is reached.At any given time, only one instance of the External Integration is active. The subsequent instance does not begin until the current instance completes.
The same exit condition evaluates at the end of each instance; however, value(s) of the Request variable(s) used in the exit condition can change during an instance resulting in the exit condition to eventually evaluate as
True.If any one instance of that External Integration does not complete, workflow pauses.
All active instances are terminated if an interrupting boundary-type event element triggers.
An element configured in this mode shows the Loop icon
 in Process Modeler.
in Process Modeler.
Multi-instance (Parallel): Select the Multi-instance (Parallel) option to perform this External Integration multiple times in parallel a fixed number of times. This is useful when performing any action in bulk, such as sending an email to several people. This loop mode has the following characteristics:
Instances of the External Integration are governed by the size of an array-type Request variable where a new instance is created for each item in this variable. For example, an array with 10 items will create 10 parallel instances of this External Integration that each contains data from its respective array index.
All instances begin simultaneously when this element triggers; however, they perform their External Integration independently of each other.
The External Integration as a whole completes when all instances are complete.
The output from each instance can either be saved in the source Request variable or a new array-type Request variable.
All active instances terminate if an interrupting boundary-type event element triggers.
An element configured in this mode shows the Multi-instance (Parallel) icon
 in Process Modeler.
in Process Modeler.
Multi-instance (Sequential): Select the Multi-instance (Sequential) option to perform this External Integration multiple times sequentially a fixed number of times or until an exit condition is
True. This is useful when sequentially repeating a External Integration multiple times but with a different set of data each time. This loop mode has the following characteristics:Instances of the External Integration are governed by the size an array-type Request variable where a new instance is created for each item in this variable. For example, an array with 10 items will create 10 parallel instances of this External Integration that each contains data from its respect array index.
At any given time, only one instance of the External Integration is active. The subsequent instance does not begin until the current instance completes.
At the end of each instance an exit condition evaluates and the loop activity halts if the exit condition is
True.The External Integration as a whole completes when all instances are complete.
The output from each instance can either be saved in the source Request variable or a new array-type Request variable.
All active instances terminate if an interrupting boundary-type event element triggers.
An element configured in this mode shows the Multi-instance (Sequential) icon
 in Process Modeler.
in Process Modeler.
Follow these steps to specify characteristics to perform multiple instances of the External Integration:
Select the element from the Process model in which to specify multiple instance characteristics.
Ensure that the Configuration panel displays. If not, show it. Panels to configure this External Integration display.
Expand the Loop Characteristics panel. The Loop Characteristics setting displays. By default, Loop Activity is set to No Loop Mode and the External Integration is performed only once.
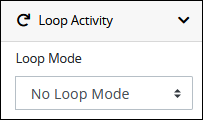
From the Loop Mode setting, select one of the following options to perform this External Integration more than once.
Loop: Select the Loop option. The settings for this loop mode display:
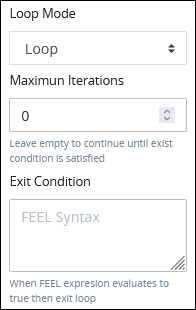
Follow these steps:
In the Maximum Iterations setting, enter an integer value representing the maximum number of times this External Integration should be performed.
In the Exit Condition setting, enter a condition in FEEL syntax. When this condition is True the loop activity is halted.
Multi-instance (Parallel): Select the Multi-instance (Parallel) option. The settings for this loop mode display:
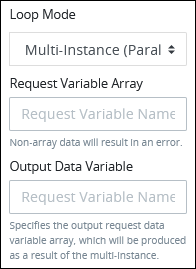
Follow these steps:
In the Request Variable Array setting, enter the name of an array-type Request Variable. The size of this array will determine how many times this loop iterates.
In the Output Data Variable setting, enter the name of an array-type Request variable in which to store the results of all instances. Each instance of the loop saves to a separate JSON object within the array of the specified Request variable. If the Output Data Variable setting is not configured, then the output data replaces the source data in the Request Variable Array.
Multi-instance (Sequential): Select the Multi-instance (Sequential) option. The settings for this loop mode display:

Follow these steps:
In the Request Variable Array setting, enter the name of an array-type Request Variable. The size of this array will determine how many times this loop iterates.
In the Exit Condition setting, enter a condition in FEEL syntax. When this condition is True the loop activity is halted.
In the Output Data Variable setting, enter the name of an array-type Request variable in which to store the results of all instances. Each instance of the loop saves to a separate JSON object within the array of the specified Request variable. If the Output Data Variable setting is not configured, then the output data replaces the source data in the Request Variable Array.
Query Panel Settings
Enter SQL Queries
Enter SQL queries to interact data with the External Integration such as storing, manipulating and retrieving data.
Follow these steps to enter SQL queries:
Select the connector from the Process model.
Ensure that the Configuration panel displays. If not, show it. Panels to configure this element display.
Expand the Query panel if it is not presently expanded. The SQL setting displays.
In the SQL setting, enter queries to interact with the External Integration.
Optionally, click
 at the top right of the setting to open the Query window where you can enter queries.
at the top right of the setting to open the Query window where you can enter queries. 
Press enter to save queries.
Response Mapping Panel Settings
Map Data from the Data Source to the Request's JSON Data Model
Configure how data from the External Integration source integrates with Request data.
The procedure to integrate the data source's data to the Request JSON data model is called response mapping: specifying into which Request variable to store the data source's data. The External Integration may be configured with response mapping, whereby a specified source name in the body or header of the data source response's is mapped to store that value in a specified Request variable. By relying on the External Integration's response mapping, the Process Designer only needs to select the Request variable name as mapped in the External Integration's response without knowing technical details for this mapping.
Each JSON object contains a key name that references the JSON object, and the value for that key. If the JSON object already exists in a Request's JSON data model, then the External Integration overwrites the existing JSON object value with that from the data source. If the JSON object(s) to map the data source data does not exist, then the External Integration adds the JSON data object(s) to that Request's JSON data model.
Follow these steps to specify the Request JSON data object(s) to which to map the data source's data:
Select the External Integration from the Process model to map the data source's data to the Request JSON object(s).
Ensure that the Configuration panel displays. If not, show it. Panels to configure this element display.
Expand the Response Mapping panel if it is not presently expanded. The Response Mapping setting displays.

Click the
 icon to add a JSON object to which to map data from the data source. The Source and Set to Request Variable settings display to add the JSON source name and its variable, respectively, for the JSON object.
icon to add a JSON object to which to map data from the data source. The Source and Set to Request Variable settings display to add the JSON source name and its variable, respectively, for the JSON object.
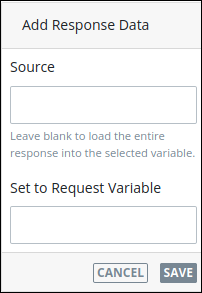
In the Source setting, enter the name of the source from which to store the response. If the source is from Request data, such as from a Collection, the source name is
data.datais the name of the JSON object that stores all data for each Request. However, the Source setting corresponds with how the External Integration maps the data response: by selecting a mapped Request variable from the Set to Request Variable setting below, its corresponding source name displays in the Source setting. Optionally, specify the source name as a Request variable using mustache syntax.In the Set to Request Variable setting, enter the Request variable as configured in the External Integration's response mapping in which to store the data source's response. Optionally, specify the source name as a Request variable using mustache syntax. After doing so, the Source setting displays the source's name configured for that response mapping.
Click Save.
Repeat Steps 4 through 6 for each Request variable to store the data source's response.
Click the Delete icon![]() to delete a mapped response from the Response Mapping setting.
to delete a mapped response from the Response Mapping setting.
Error Handling Panel Settings
Edit Timeout and Retry Settings When Errors Occur
Follow these guidelines to set how to handle External Integration runtime errors:
Set how many seconds to wait when an unexpected error occurs during runtime before displaying the error in that connector, thereby causing that Request to be in Error status.
Set how many consecutive attempts to run the connector before displaying a runtime error.
Requests are going to wait the configured number of seconds and consecutive runtime attempts for an unresponsive connector before displaying the error.
Optionally, notify the Process Manager of the External Integration runtime error via an in-platform or email notification.
Follow these steps to edit the Error Handling settings for a External Integration:
Select the External Integration from the Process model in which to edit the Error Handling.
Ensure that the Configuration panel displays. If not, show it. Panels to configure this External Integration display.
Expand the Error Handling panel if it is not presently expanded. The Timeout setting displays.

In the Timeout setting, configure how many seconds to wait for an unresponsive External Integration before declaring a time-out as follows:
Enter the number of seconds. Use the up and down arrows to increase or decrease seconds.
Set
0for no timeout.Leave empty to use the External Integration default setting.
In the Retry Attempts setting, configure how many times to re-execute the External Integration if the connector returns a runtime error as follows:
Enter a number. Use the up and down arrows to increase or decrease the number.
Set
0for no retry attempts.Leave empty to use the External Integration default setting.
In the Retry Wait Time setting, configure how many seconds to wait before attempting a retry as follows:
Enter the number of seconds. Use the up and down arrows to increase or decrease seconds.
Set
0for no timeout.Leave empty to use the External Integration default setting.
Enable the In-app Notification toggle to notify through the user interface to the Process Manager that there is a External Integration runtime error.
Enable the Email Notification toggle to notify through an email to the Process Manager that there is a External Integration execution error.
Documentation Panel Settings
Edit the External Integration's Description Displayed in Process Documentation
Describe the External Integration's purpose and how it functions in the Process. This description does not affect Requests for the Process, but may be useful for Process model maintenance such as how the connector is configured. Edit information by using the What-You-See-Is-What-You-Get (WYSIWYG) rich text editor.
A Process's entered documentation displays by selecting the View Documentation icon for that Process.
Follow these steps to edit the description for an External Integration:
Select the External Integration from the Process model in which to edit its description.
Ensure that the Configuration panel displays. If not, show it. Panels to configure this External Integration display.
Expand the Documentation panel if it is not presently expanded. The Description setting displays.
In the Description setting, edit the information to display when viewing documentation for this External Integration and then press Enter. Alternatively, use the What-You-See-Is-What-You-Get (WYSIWYG) rich text editor to stylize your text by clicking the More icon
 .
.
Follow these guidelines to use the WYSIWYG rich text editor to stylize your text:
Undo changes: Click on the
 icon to undo the last action.
icon to undo the last action.Redo changes: Click on the
 icon to redo the last undone action.
icon to redo the last undone action.Insert/Edit Link: Click on the
 icon to convert the selected text into a hyperlink. Follow these steps to create a hyperlink:
icon to convert the selected text into a hyperlink. Follow these steps to create a hyperlink: Select the required text from the Rich Text control.
Click on the
 icon. The Insert/Edit Link screen displays.
icon. The Insert/Edit Link screen displays. .png)
In the URL setting, enter the destination URL.
In the Text to display setting, edit or enter the text displayed in the Rich Text control.
In the Title setting, enter the text to display when a user hovers over the displayed text.
From Open link in… drop-down menu, select one of these options:
New window: Select this option to open the destination page in a new browser window.
Current window: Select this option to open the destination page in the current browser window.
Insert/Edit Image: Click on the Insert/Edit Image icon
 to insert an image. Follow these guidelines:
to insert an image. Follow these guidelines: Click on the Insert/Edit Image icon
 .
. The Insert/Edit Image screen displays:
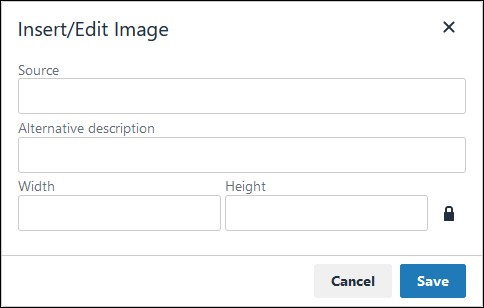
In the Source setting, enter a URL for the image.
In the Alternative Description setting, enter the text to display if the source URL of the image is not accessible.
In the Width setting, enter the maximum width for the image.
In the Height setting, enter the maximum height for the image.
Toggle the Constrain Proportions icon
 to maintain the width-height ratio of the image to its original proportion.
to maintain the width-height ratio of the image to its original proportion. Click Save.
Insert Page Break for PDF: Click on the Insert Page Break for PDF icon
 to insert a page break when a PDF document is created for this documentation if your browser supports this feature.
to insert a page break when a PDF document is created for this documentation if your browser supports this feature. Format text: Follow these guidelines to format text:
Headings: From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Headings and then select a heading size.
Bold: Do one of the following:
From the editor toolbar, select the
 icon.
icon.From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Inline and then Bold.
Italics: Do one of the following:
From the editor toolbar, select the
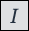 icon.
icon.From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Inline and then Italic.
Underline: From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Inline and then Underline.
Strikethrough: From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Inline and then Strikethrough.
Superscript: From the Paragraph/ Formats menu, select Inline and then Superscript.
Subscript: From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Inline and then Subscript.
Code: From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Inline and then Code.
Paragraph: From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Blocks and then Paragraph.
Blockquote: From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Blocks and then Blockquote.
Division: From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Blocks and then Div.
Preformatted: From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Blocks and then Pre.
Change text color: Use the Text Color drop-down to change text color. Click on the
 icon. The color palette displays. Do one of the following:
icon. The color palette displays. Do one of the following:Select one of the color swatches from the color palette. The selected text changes to that color.
Click the
 icon to select a custom color from the Color Picker.
icon to select a custom color from the Color Picker.Click the
 icon to reset the text to its default color.
icon to reset the text to its default color.
Align text: Follow these guidelines to align text:
Left align: Do one of the following:
From the editor toolbar, use the
 icon to left-align text.
icon to left-align text.From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Align and then Left.
Center align: Do one of the following:
From the editor toolbar, use the
 icon to center-align text.
icon to center-align text.From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Align and then Center.
Right align: Do one of the following:
From the editor toolbar, use the
 icon to right-align text.
icon to right-align text.From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Align and then Right.
Justify: Do one of the following:
From the editor toolbar, use the
 icon to justify text.
icon to justify text. From the Paragraph/Formats menu, select Align and then Justify.
Insert a bullet list: Use the
 icon to format text as a bulleted list.
icon to format text as a bulleted list.Insert a numbered list: Use the
 icon to format text as a numbered list.
icon to format text as a numbered list.Indent text: Click on the
 icon to increase text indenting.
icon to increase text indenting.Outdent text: Click on the
 icon to decrease text indenting.
icon to decrease text indenting.
Advanced Panel Settings
Edit the Node's Identifier Value
A Process node represents a component of a Process model, including any of its objects. Process Modeler automatically assigns a unique value to each Process node added to a Process model. A Process node's identifier value can be changed if it is unique to all other nodes in the Process model, including the Process model's identifier value.
All identifier values for all nodes in the Process model must be unique.
Follow these steps to edit the identifier value for an External Integration:
Select the External Integration from the Process model in which to edit its identifier value.
Ensure that the Configuration panel displays. If not, show it. Panels to configure this External Integration display.
Expand the Advanced panel if it is not presently expanded. The Node Identifier setting displays. This is a required setting.
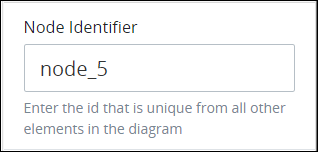
In the Node Identifier setting, edit the External Integration's identifier to a unique value from all nodes in the Process model and then press Enter.